
A rising number of businesses now trust machine learning as part of artificial intelligence. There are way too many specifics. The ability to efficiently manage global functions comes in first. A supply chain would not make sense if it had to be managed globally. Consider the expense and asset required. You'll never have operations free of bugs. Human mistake is possible with these techniques.
The amount of information in the supply chain is increasing its complexity. DHL manages analytic system management in their supply chain using artificial intelligence and machine learning. This skill can determine the most frequent reasons for shipment delays by analyzing 58 different types of internal data.
Artificial intelligence is overtaking human expertise in supply chain management and global logistics. Many executives in the transportation sector predict that these areas will experience more profound change. As a result of the continual development of technologies like big data and artificial intelligence, many industries are open to disruption and innovation.
Calculating algorithms used in artificial intelligence assists you in choosing from a big amount of information made up of logistics and supply chains. These techniques can be applied and their potential effects on procedures or composite functions can be investigated.
Introduction
The number of AI applications has considerably expanded during the last few years. Also, the adoption of AI has accelerated year after year. All sectors and domains have used these technologies. The rate of adoption varies from industry to industry, though. The primary driver of AI adoption is the technology's favorable effects on economic growth. It is important to pay close attention to how industrial AI is being adopted in the context of Industry 4.0. Since AI touches many important industries, including manufacturing, retail, and transportation, it is imperative to consider it in the context of Supply Chain Management (SCM).
The Impact Of AI On The Supply Chain

Before we can critically assess the impact of AI in SCM, let's briefly examine the impact of AI on the related sectors.
Manufacturing: Impact
Manufacturing is the industry that is most interested in adopting and integrating AI, aside from technology. Manufacturing has the greatest Industry 4.0 applications overall, according to research. At first glance, this could seem counter intuitive. Manufacturing is a capital-intensive industry that needs careful consideration. When analyzing the adoption of new technology, cost-benefit analysis is frequently the most risk-averse. It's crucial to remember that efficiency and quality are highly valued in the manufacturing sector.
Players in the industry are very competitive because they desire more attention. The sector's leading policymakers are more interested in technical backgrounds and scientific theories. This enables the sector to embrace more cutting-edge technical solutions or procedures. These elements played a significant role in the manufacturing industry, being one of the first to adopt AI. It is also important to note that the manufacturing sector has incorporated AI into its operations, contributed to the field, and filled voids.
The following are SCM's top picks for AI uses that have significantly impacted the manufacturing industry.
- Predictive upkeep: Although predictive maintenance has existed for more than 20 years, its usefulness has grown as AI technology has advanced, got compiled and MAP saved.
- ML engines: can be used for generative design to produce designs. Practical uses of ML engines have lowered turnaround times and expanded the number of available designs. Using ML engines has made it possible to create original designs.
- Robotics: Although manufacturing has used robotics, AI advancements have created new opportunities in this field. One of the first robotic arms for industrial application is one. Additive manufacturing with cloud-based robots.
- Edge analytics: The extensive use of sensors in machines to acquire real-time data is one of the Internet of things' finest applications in the manufacturing sector. According to the report, the data can be used for several things, like scheduling or access control, Edge analytics can be further enhanced with AI/ML through the effective utilization of large data.
Remember that these adoptions might not always be mature enough or highly efficient. There are also big problems. It is conceivable to anticipate AI.
Retail Impact
SCM sees sales prediction as the most important use of AI in retail. implemented deep learning models for retail sale prediction for the first time, and they have since become widely used. This represents the development rate in applying models to analyze unstructured data.
Impact on logistics
The SCM sees AI as a huge opportunity in the following areas:
Predictive analytics: Predictive Analytics supports decision-making by assisting businesses in managing heterogeneous processes and bringing transparency. Big data is employed in this more specialized method. However, predictive analytics can also be combined with deep learning models to increase prediction.
Placement of transportation assets: Decision-makers can gain significant insight into the placement of future transportation assets by utilizing sensors, network connections, big data, and, finally, deep learning. Managers of supply chains benefit greatly from this skill, the market for AI in transportation will reach $10.3 billion by 2030.
Last-mile delivery: To address last-mile delivery issues, AI has been widely deployed. AI will be applied more frequently in these situations as it promotes sustainability.
A Holistic View
AI is making steady inroads into sectors in which SCM is heavily involved. It is now important to examine the use of AI in supply chains' core: SCM. AI's long-standing history had not been fully exploited in the SCM space. SCM areas where AI could be used:
- Planning and inventory control
- Transportation network design
- Supply and purchasing management
- Forecasting and demand planning
- Problems with order-picking
- Management of customer relationships
- e-synchronized SCM
This extensive list can be used as a reference. As indicated earlier, Demand and transportation planning made substantial use of AI. A defined customer engagement team assisted by automated procedures, AI engines, and other tools manages customer interactions better. They don't necessarily have anything to do with supply chain management. As a result, it won't be covered in this report. The time to examine the remaining items is now.
The Growth Of AI's Influence On SCM

It's crucial to remember that not all industries are equally equipped for AI. Because of this, it is challenging to predict the development of the use of AI in SCM across various organizations. Although having a significant SCM focus, for instance, will have the same applicability in SCM scenarios.
Helpful framework for determining the sector's overall tendencies and making the necessary adjustments, in considering competitor activity during the Observe phase. The activities of competitors will instill a feeling of urgency because delaying the adoption of suitable AI-based tools or solutions might negatively damage an organization's competitiveness.
This analysis of competitors' adoption of AI-based solutions must be thorough and consider several fields.
- Plan
- Distribution and logistics
- Production
- Procurement
- Marketing and sales
These evaluations will help business leaders make judgments and take appropriate action. Automation will undoubtedly lead to a rise in adoption across all sectors. Major changes are being faced by organizations. It is anticipated that adoption will spread a wide range. By 2026, more than 75% of commercial suppliers of programs for supply chain management will incorporate advanced analytics, AI, and data science. A crucial reminder is provided, which showed early-stage AI demonstrations and anticipated that the technology would develop at least ten years later.
Although not all technologies in the hype cycle are successful, it is still reasonable to believe that AI will advance given its exponential development rate. AI is anticipated to be a major technological driver, due to the accessibility of less expensive computing resources for consumers and businesses, as well as substantial focus and attention from both government and corporate governance, if not the biggest.
It's starting to get fascinating. While AI models and AI engines can assist human managers in making better judgments, is it possible for AI engines that make tactical decisions in SCM as well? According to a report, cognitive automation is an application that can foresee outcomes and make supply chain decisions independently as long as it follows established business rules and constraints. Advanced technology like self-driving supply chains results from this. Although they may not be strategically sound, these choices muddy the distinction between strategy and tactics in the current global environment.
The Extent Of Ai-Based Decision-Making Within SCM
When the epidemic began, there were significant disruptions to the supply chain. The situation is equally as complicated when you look at the classification of industries. It is clear that it is reliant on the semiconductor industry. Nonetheless. What proportion of cognitive automation is appropriate for SCM decision-making? This question can be answered by going over some of the most important components of this context once more.
The Consequences Of Cognitive Automation
Intelligent agents must be able to recognize the layout of their surroundings and foresee potential changes. They must also differentiate between desired and undesired changes. The most important aspect of decision-making in his seminal study on AI. While cognitive automation can make decisions within predetermined limits, identifying such limits or, in the worst situations, realizing that they can shift over time are challenges.
Cognitive automation can be employed to learn about contract or spot market procurement. Yet, these laws might not be relevant in real life due to geopolitical uncertainties. Losing your employment is a possibility that is always present.
Adding Redundancy To Rules
Redundancy can occasionally be a fantastic option, but it can also be incredibly expensive. Although redundant supply chain strategies might "buy time" for businesses to recover from interruptions, there are accompanying costs, such as tying up cash in inventory or higher transaction costs from managing several suppliers. When ethics are considered while making decisions, these expenses can soon become prohibitive.
The Ethics Behind Decision-Making

Monitoring and putting ethical sourcing and manufacturing into practice is already challenging. The implementation and oversight of these policies are equally challenging. Responsible AI must consider ethics in design, development, and designing. Suppose only one choice is chosen, like the disclosure policy for sourcing. In that case, it is obvious that this choice is influenced by the cost of disclosure, the gain or loss of market share, the original market shares, the likelihood of discovery, and the margin contribution.
Even in tactical situations, the decision-making process that only relies on cognitive automation can be exceedingly complex and potentially hazardous for businesses. Any choice that potentially has an impact on a company must involve a human,
Big Data And AI Are Used In The Supply Chain

Business intelligence is a common tool companies use to manage their operations and streamline intricate supply chains. These plans rely on "post-mortem information," an extremely old data type. These processes must be finished, used, and verified for task gaps before they can be enhanced.
With the introduction of big-data development services, this "pause" in job inspection has almost completely disappeared. Artificial intelligence in the supply chain has allowed employers to analyze transactional data within their processes proactively. These visions can be employed to identify errors and task gaps immediately. So, the responsiveness of big data in the supply chains helps avert revenue losses. Let's examine the supply chain management order-to-cash cycle. The shipping may be interrupted, which may take up to 70 days. Several stages may be paused due to this disruption, and several trials may be initiated.
Without big data analytics, it might be challenging to identify what caused the outage. Yet, you're in charge of the supply chain. In that case, AI Development Companies can anticipate these disruptions in advance and decide how to work around them. You could also limit profits losses due to canceled or refunded orders.
How Can You Improve The Supply Chain With Big Data And Artificial Intelligence?

Aside from the amazing rise in information volumes and algorithmic advancements, big data interaction and speed have propelled artificial intelligence into the supply chain. These are the most significant applications of artificial intelligence that can be made in supply chain management. This post will review a few strategies commercial organizations may use to use artificial intelligence to succeed in the supply chain.
Reduce Your Costs
Big data and artificial intelligence-based combination algorithms can be utilized to resolve the complex delivery and charging issues that many firms are currently facing. By developing the appropriate ML model, a company can receive important insights on enhancing and growing its supply chain performance. Businesses may cut their losses by applying artificial intelligence and machine learning to stop abnormalities in logistics expenses.
Read More: Big Data Analytics Benefits - How To Analyse Big Data
Companies can capture images of cargo to identify any damage and take the necessary corrective action instantly. Artificial intelligence technologies, such as AI powered graphic Inspection, make this possible.
Optimizing And Improving Logistics

A logistics company can utilize artificial intelligence to enhance each of its processes, from picking and gathering goods to shipping and receiving them. Big data has enormous potential to lower logistics costs while simultaneously improving skills. Cloud Infrastructure Solutions focuses on thought leadership and cloud computing skills.
It entails identifying and examining designs in track-and-trace data that was gathered using sensors compatible with the Internet of things.
Another significant logistics solution using artificial intelligence solution is intelligent robotic sorting. This technology is employed in supply chain optimization and logistics organization. It can sort letters, messages, and deliveries accurately, promptly, and successfully.
Forecast Accuracy: Bringing Accuracy To The Demand
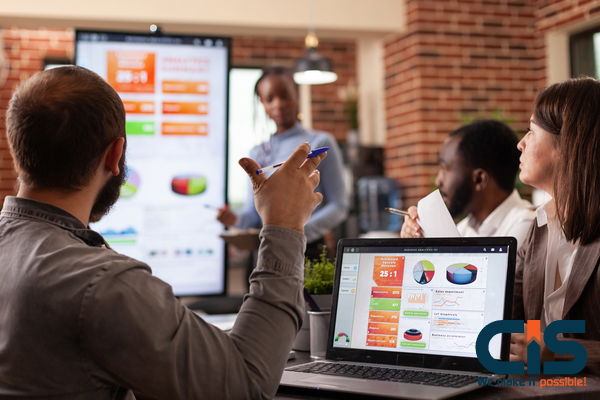

The demand side is imbalanced and ambiguous, raising many concerns about the supply chain. Before the development of artificial intelligence, removing all costs from supply chains was impossible. Accounting for various client traits proved challenging.
The use of artificial intelligence for request prediction has greatly simplified things. The supply chain is being redesigned with data, visions, and the capacity to observe the request side. Big data and artificial intelligence make it possible to determine the most effective ways to address issues ranging from item growth to request preparation.
Among the many options, automatic classification and drone-compatible account systems are just a few. The supply chain's big data has made Demand can be easily predicted. A great example of artificial intelligence in demand prediction is seen in Amazon's computerized delivery facilities.
Stimulating Supplier Relationships

When selecting the best supplier, logistics professionals need to be cautious. The reputation of your entire business depends on how capable and efficient your supplier is.
Several logistic business units shifted to clever artificial intelligence-based solutions to lower the risk of dealers. To calculate credit count, artificial intelligence can examine a large amount of data about dealers. The "dullness of suppliers" can then be assessed using this. They can see which suppliers have the lowest rate of fraud and which item centers are best at finding defects. The business can choose its suppliers more wisely.
Customer Experience Improvement

A research team that analyzes the effects of training employees in supply chain jobs believes that artificial intelligence has raised customer service to a new level.
The ability of intelligent technologies to carry out straightforward, uncomplicated tasks without the threat of fraud will increase consumer consumption rates. Artificial intelligence has made it possible to personalize. DHL uses the Amazon system to provide a voice-based service for tracking deliveries and packages. Consumers can easily obtain the necessary information by asking Alexa questions about their orders.
What Can Artificial Intelligence Do For Retail Operations?

Thanks to big data and artificial intelligence, retailers can study trends from prior purchases and shopping periods. To forecast which products will be the most in Demand in the future, this is put together with current purchasing patterns. Shops can improve potential customer happiness and product availability by increasing visibility in multiple activities like purchase orders, shipments, and list reports. To assure product availability, vendors should have better and more timely information. This will raise downstream sales and aid in increasing customer satisfaction, customer preferences.
Want More Information About Our Services? Talk to Our Consultants!
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence in supply chains has countless advantages that are unmatched. Spreadsheets should no longer be used to manage requests and supplies. Utilize your data to foresee and steer clear of circumstances that can make you worry that the list won't sell or will come apart.
To receive assistance with request prediction, record rebalancing, record replacement, and forced list replacement, join the artificial intelligence solutions and big-data trend. Your supply chain can only be made better with artificial intelligence.


